Chinese Electric Vehicle Brands on Southeast Asian Market: Operation Analysis
Chinese electric vehicle manufacturers are making significant strides in entering and expanding within the Southeast Asian market through strategic partnerships, local manufacturing, competitive pricing, and investments in infrastructure. Their efforts are supported by favorable government policies and a growing consumer interest in sustainable transportation solutions. As these companies continue to innovate and adapt to local market needs, their presence in Southeast Asia is likely to grow, contributing to the region’s shift towards electric mobility.
Chinese Electric Vehicle Brands on Southeast Asian Market:
1. BYD (Build Your Dreams)
- Operations in Southeast Asia:
- Thailand: BYD has entered the Thai market with its electric buses and has been exploring opportunities for passenger vehicles.
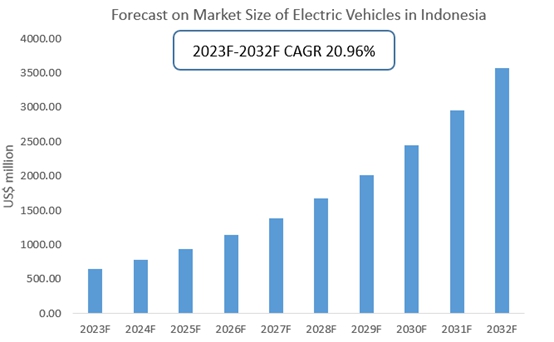
- Indonesia: BYD has partnered with PT Bakrie & Brothers to produce electric buses and has signed agreements for supplying EVs to various local transport authorities.->Indonesia Electric Vehicle Industry Research Report 2023-2032
- Philippines: BYD has introduced its electric taxis and buses, focusing on urban public transportation. ->Philippines Electric Vehicle Industry Research Report 2023-2032
- Key Projects and Partnerships:
- Jakarta’s Electric Buses: BYD has supplied electric buses to Jakarta’s TransJakarta bus rapid transit system, contributing to the city’s efforts to reduce emissions.
- Partnerships: Strategic collaborations with local firms for assembly and distribution, such as with Bakrie & Brothers in Indonesia.
- Products: A range of electric vehicles including electric buses, taxis, and passenger cars like the BYD e6 and Tang EV.
2. Great Wall Motors (GWM)
- Operations in Southeast Asia:
- Thailand: GWM has established a manufacturing facility in Rayong, Thailand, acquired from General Motors. The plant produces various models including the Haval H6 Hybrid and the Ora Good Cat EV.
- Key Projects and Partnerships:
- Rayong Plant: The Rayong facility serves as GWM’s manufacturing hub for the region, focusing on both internal combustion engine vehicles and electric vehicles.
- Marketing and Distribution: GWM has launched several marketing campaigns to build brand awareness and partnered with local dealerships for distribution.
- Products: Focus on SUV models and electric vehicles like the Haval series and Ora Good Cat, catering to diverse consumer needs.
3. Wuling Motors
- Operations in Southeast Asia:
- Indonesia: Wuling has a significant presence in Indonesia with a local assembly plant in Bekasi, West Java. The plant produces the popular Wuling Confero and Cortez series, as well as the Wuling Hongguang Mini EV.->Indonesia Electric Vehicle Industry Research Report 2023-2032
- Key Projects and Partnerships:
- Local Production: Wuling’s assembly plant in Bekasi produces vehicles for both domestic use and export, supporting Indonesia’s automotive industry growth.
- EV Launch: Introduction of the Wuling Hongguang Mini EV in Indonesia, a small, affordable electric vehicle aimed at urban commuters.
- Products: Known for the Wuling Hongguang Mini EV, which has gained popularity due to its affordability and practicality for city driving.
4. NIO
- Operations in Southeast Asia:
- Exploratory Phase: NIO is in the initial stages of entering the Southeast Asian market, focusing on understanding local consumer preferences and regulatory environments.
- Key Projects and Partnerships:
- Potential Collaborations: NIO is exploring partnerships with local companies for distribution and charging infrastructure development.
- Products: Premium electric vehicles such as the ES8, ES6, and EC6, which focus on high-performance and advanced technology.
5. Geely Auto Group
- Operations in Southeast Asia:
- Malaysia: Geely has a strategic stake in Malaysia’s Proton Holdings, enabling it to expand its footprint in the Southeast Asian market.
- Key Projects and Partnerships:
- Proton Partnership: Geely’s partnership with Proton includes technology transfer and production of jointly-developed vehicles, including hybrid and electric models.
- New Models: Introduction of models like the Proton X70 and plans to introduce electric variants in the near future.
- Products: Focus on hybrid and electric vehicles through the Proton brand, leveraging Geely’s technology and Proton’s market presence.
6. SAIC Motor Corporation
- Operations in Southeast Asia:
- Thailand: SAIC has partnered with the CP Group to form SAIC Motor-CP, producing and selling MG-branded vehicles.
- Key Projects and Partnerships:
- MG ZS EV: Launch of the MG ZS EV in Thailand, an affordable electric SUV that has seen positive market reception.
- Expansion Plans: SAIC is planning further investments to expand its production capacity and introduce more EV models in the region.
- Products: A range of MG-branded vehicles, including the MG ZS EV and MG EP, catering to the growing demand for electric mobility.
7. XPeng Motors
- Operations in Southeast Asia:
- Exploratory Market Entry: XPeng is evaluating the market potential in Southeast Asia, focusing initially on building brand awareness and understanding consumer needs.
- Key Projects and Partnerships:
- Pilot Programs: XPeng has initiated pilot programs to introduce its models to the Southeast Asian market, focusing on urban mobility solutions.
- Strategic Alliances: Potential collaborations with local firms for distribution and after-sales services.
- Products: Premium electric vehicles such as the XPeng P7 and G3, known for their advanced technology and autonomous driving capabilities.
Challenges and Considerations
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating different regulations and standards across Southeast Asian countries can be complex and requires thorough understanding.
- Consumer Awareness: Raising awareness and educating consumers about the benefits of EVs is essential for market penetration.
- Infrastructure Development: The success of EV adoption is closely tied to the availability and reliability of charging infrastructure.
How Chinese Electric Vehicles Enter the Southeast Asian Market
1. Strategic Partnerships and Joint Ventures
- Local Collaborations: Chinese EV companies often partner with local automotive firms to gain market insights, distribution networks, and regulatory compliance assistance. For example, BYD has partnered with PT Bakrie & Brothers in Indonesia to produce electric buses.
- Joint Ventures: Establishing joint ventures with Southeast Asian companies allows Chinese EV manufacturers to share technology, reduce risks, and tap into established customer bases.
2. Building Manufacturing Facilities
- Local Production: Setting up manufacturing plants in countries like Thailand and Indonesia helps Chinese EV makers reduce production costs, avoid import tariffs, and benefit from local incentives.
- Employment Opportunities: By creating jobs and investing in local economies, these companies gain favorable positions with governments and consumers.
3. Government Incentives and Policies
- Tax Incentives and Subsidies: Many Southeast Asian governments offer incentives such as tax breaks, subsidies, and grants to attract foreign EV investments. Chinese companies take advantage of these to reduce operational costs.
- Support for EV Adoption: Policies promoting EV usage, such as reduced registration fees and free public charging, further aid Chinese EV firms in market entry and expansion.
4. Market-Specific Models
- Adaptation to Local Needs: Chinese EV manufacturers develop models tailored to the specific needs and preferences of Southeast Asian consumers, such as affordable pricing, smaller vehicle sizes, and features suited to local driving conditions.
- Diverse Product Range: Offering a wide range of EVs from budget-friendly options to high-end models allows Chinese firms to cater to various market segments.
5. Building Charging Infrastructure
- Collaborative Efforts: Partnering with local governments and private companies to develop and expand charging infrastructure is crucial. NIO, for example, collaborates with local entities to establish battery swapping stations.
- Investment in Infrastructure: Direct investment in building charging stations helps alleviate range anxiety and promotes EV adoption.
6. Aggressive Marketing and Branding
- Localized Marketing Campaigns: Tailoring marketing strategies to resonate with local cultures and values helps Chinese EV brands gain consumer trust and recognition.
- Sponsorships and Events: Participating in local events, sponsoring eco-friendly initiatives, and showcasing at auto shows enhance brand visibility and credibility.
7. Competitive Pricing
- Affordable Options: Offering competitively priced EVs makes them accessible to a broader audience. Brands like Wuling have introduced cost-effective electric mini-cars in the region.
- Financing and Leasing Plans: Flexible financing options and leasing plans make it easier for consumers to switch to electric vehicles.
8. Technology Transfer and R&D Investment
- Local R&D Centers: Establishing research and development centers in Southeast Asia helps adapt technologies to local conditions and fosters innovation.
- Knowledge Transfer: Collaborating with local universities and research institutions promotes technology transfer and enhances the skill set of the local workforce.